
Der Unterschied zwischen 304 Edelstahlguss Und 316 Edelstahl Casting beginnt mit ihrem chemischen Make -up. 316 Edelstahl umfasst Molybdän, das seine Festigkeit gegen Rost und harte Bedingungen stärkt. Viele Branchen wählen Edelstahl -Investitionsguss Für Teile, die dauern müssen, abhängig von den Anforderungen des Jobs.
Key Takeaways
- 304 Edelstahlguss offers good rust resistance and works well for everyday indoor uses like kitchens and food processing.
- 316 stainless steel casting contains molybdenum, which makes it stronger against corrosion, especially in salty or harsh chemical environments.
- Choose 304 for budget-friendly projects in mild conditions; pick 316 for marine, chemical, or outdoor parts that need extra durability.
The difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting: Definitions

What is 304 stainless steel casting?
304 Edelstahlguss is one of the most common types of stainless steel used around the world. People choose it for its strong resistance to rust and its ability to handle many different jobs. When foundries make 304 stainless steel castings, they melt down the metal and pour it into molds to create parts with precise shapes.
Here’s a quick look at how different countries and standards refer to 304 stainless steel:
| Region/Standard | Bezeichnung | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| USA (AISI) | 304 | Common American industrial standard |
| Europe (EN) | 1.4301 | Widely used European standard |
| Japan (JIS) | SUS 304 | Standard Japanese designation |
| UK (BS) | 304S15 | British stainless steel standard |
| USA (SAE) | 30304 | Automotive and aerospace standard |
| USA (ASTM) | A276 | Specification for stainless steel bars and shapes |
| Germany (DIN) | 1.4301 | German standard, equivalent to EN 1.4301 |
The main ingredients in 304 stainless steel include iron, chromium (about 18-20%), and nickel (about 8-10.5%). Other elements like carbon, manganese, and silicon are kept low to help the metal stay tough and easy to work with. The chart below shows the maximum content of each main element:
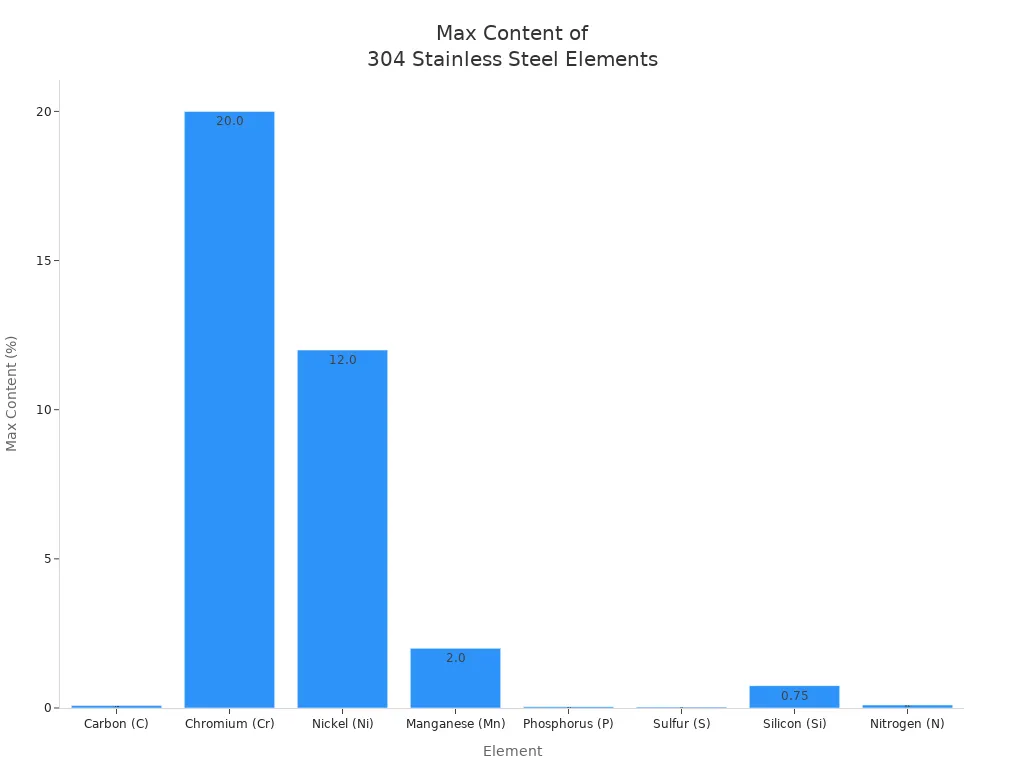
Chromium helps the metal resist rust, while nickel makes it stronger and easier to shape. Because of this mix, 304 stainless steel castings work well in kitchens, food factories, and many machines. The difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting starts with these ingredients.
What is 316 stainless steel casting?
316 stainless steel casting is another popular choice, especially when parts need to stand up to even tougher conditions. The big difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting is that 316 contains molybdenum. This extra element gives 316 stainless steel even better resistance to corrosion, especially from saltwater or harsh chemicals.
Foundries use the same casting process for 316 as they do for 304. They melt the metal and pour it into molds to create strong, detailed parts. People often pick 316 stainless steel castings for marine equipment, chemical tanks, and medical tools. These parts need to last a long time, even when exposed to moisture or aggressive cleaning agents.
The difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting: Composition and Properties

Chemical composition comparison
When looking at the chemical makeup, the difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting stands out right away. Both types contain chromium and nickel, but 316 stainless steel has an extra ingredient—molybdenum. This small change makes a big impact.
| Element | 304 Stainless Steel (%) | 316 Stainless Steel (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium | 18.00 – 20.00 | 16.00 – 18.00 |
| Nickel | 8.00 – 10.50 | 10.00 – 14.00 |
| Molybdenum | Not present | 2.00 – 3.00 |
304 stainless steel usually contains about 18% chromium and 8% nickel. This mix works well for most everyday uses. On the other hand, 316 stainless steel has a bit less chromium but more nickel, plus 2-3% molybdenum. That molybdenum is the secret to its extra strength against corrosion. So, while both alloys look similar, the difference between 304 Edelstahlguss and 316 stainless steel casting comes down to this unique addition.
Corrosion resistance and durability
Corrosion resistance is where these two types really show their differences. 304 stainless steel does a great job fighting off rust in kitchens, bathrooms, and indoor spaces. However, when salt, chemicals, or harsh cleaners come into play, 316 stainless steel takes the lead.
Molybdenum in 316 Edelstahl boosts its ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in places with lots of salt or chemicals. This makes 316 the top choice for marine parts, chemical tanks, and outdoor equipment near the ocean. The molybdenum works by making the protective oxide layer on the steel stronger and harder to break down. Even if the surface gets scratched, 316 stainless steel can repair itself better than 304.
Tip: If a project involves seawater, pool chemicals, or strong cleaners, 316 stainless steel casting will last much longer than 304.
In marine environments, 316 stainless steel can last for decades, sometimes up to 260 years before serious damage appears. 304 stainless steel, without molybdenum, may start to show signs of wear much sooner in the same conditions. For most indoor or less aggressive settings, 304 stainless steel still offers a long lifespan and solid protection.
When it comes to strength, both types are tough, but there are some differences:
| Eigentum | 304 Stainless Steel Casting | 316 Stainless Steel Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 500-700 | 400-620 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 312 | 348 |
| Hardness (Rockwell B) | 70 | 80 |
316 stainless steel casting has a higher yield strength and hardness, which means it can handle more pressure before bending or wearing down. This makes it a better fit for heavy-duty jobs in tough environments.
Cost and typical uses
Cost often plays a big role in choosing between these two types. 304 stainless steel casting costs less because it does not contain molybdenum and has less nickel. For projects where extreme corrosion resistance is not needed, 304 is the budget-friendly option.
316 stainless steel casting costs more—sometimes 40% to 75% higher than 304. However, this extra cost pays off in places where durability and corrosion resistance matter most. Over time, using 316 can save money by reducing repairs and replacements in harsh settings.
Here are some common uses for each type:
| Stainless Steel Type | Gemeinsame industrielle Anwendungen |
|---|---|
| 304 Edelstahl | Household products (tableware, cabinets, indoor pipelines, water heaters, boilers, bathtubs), automotive parts (windshield wipers, mufflers, molded products), medical equipment, building materials, chemical industry, food industry, agriculture, ship parts |
| 316 Edelstahl | Equipment for seawater, chemical, dye, paper, oxalic acid, fertilizer production; photography; food industry; coastal facilities; ropes, bolts, nuts; automotive gears; petrochemical processing equipment; paper and pulp industry; marine environments; pharmaceuticals; surgical equipment; housings |
- 304 stainless steel casting works well for kitchen sinks, food processing equipment, and indoor piping.
- 316 stainless steel casting is the go-to for marine hardware, chemical tanks, medical tools, and outdoor fixtures near the coast.
The difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting often comes down to where the part will be used and how much corrosion resistance is needed. If the environment is mild and cost is a concern, 304 is a solid choice. For harsh, salty, or chemical-heavy settings, 316 is worth the investment.
The difference between 304 stainless steel casting and 316 stainless steel casting comes down to where each one shines. Check out this quick comparison:
| Besonderheit | 304 Edelstahl | 316 Edelstahl |
|---|---|---|
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Good for most uses | Best for harsh, salty, or chemical settings |
| Kosten | Untere | Höher |
They both last a long time, but 316’s molybdenum helps it handle tough jobs. For general projects, 304 works well. For marine or chemical areas, 316 is the better pick.
FAQ
What makes 316 stainless steel casting better for marine use?
Molybdenum in 316 stainless steel helps it resist saltwater corrosion. This makes it the top choice for boats, docks, and coastal equipment.
Can you weld both 304 and 316 stainless steel castings?
Yes, both types can be welded. 316 stainless steel needs special filler material for best results. Always clean the weld area for strong joints.
Is 304 stainless steel casting safe for food contact?
- Yes, 304 Edelstahl is food-safe.
- Many kitchens and food factories use it for sinks, counters, and utensils.
- It resists rust and keeps food clean.
